Concurrency
Concurrency in the context of REST APIs refers to the simultaneous occurrence of multiple requests.
In systems that use optimistic locking, GET, POST and DELETE methods do not typically result in concurrency problems, however, data consistency problems can occur when updating resources using PUT or PATCH methods when appropriate concurrency designs are not implemented.
Problem Statement
The following example shows how concurrency issues can arise:
- consider two users who have performed a
GETagainst a resource e.g.GET /loans/123and they both receive a payload of, for example:{amount = 1000 EUR , status= pending} - the first user then modifies the payload and requests an update to the amount with a new payload e.g.
PUT /loans/123 {amount = 1500 EUR , status= pending} - the second user also modifies the payload and requests an update to the status with a new payload e.g.
PUT /loans/123 {amount = 1000 EUR , status= approved} - if the first user commits their change first then, without concurrency controls the second user can modify the loan without knowing that the amount was changed by the first user which might result in data consistency issues
- this is a concurrency scenario issue - note that concurrency can occur for any field in the resource payload
- the solution to this problem is to ensure that one of the users is returned an error message stating that their update cannot be made
The following diagram provides an example of how concurrency problems are avoided using If-Match and ETag:
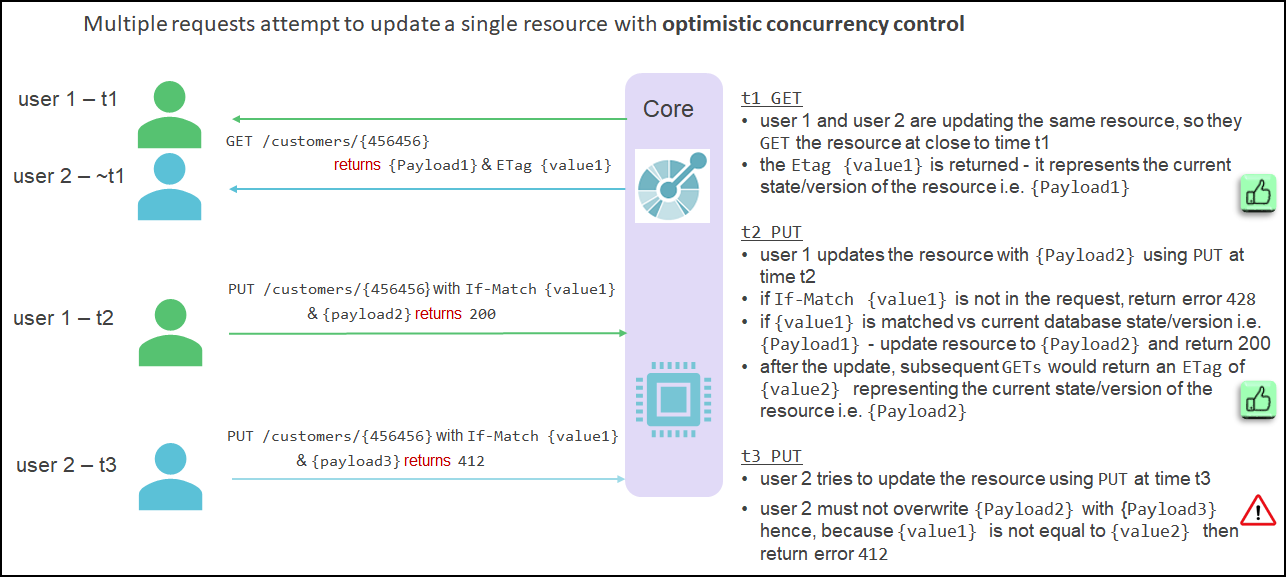
Solution
Concurrency issues can be avoided when using optimistic locking by ensuring that update operations are designed to occur only when the original payload matches the resource’s current payload. The implication of this approach in the example is that one of the users will be issued with an error message stating that the update cannot be made because the data has been modified from its state at the time of the GET by a separate unrelated update.
With REST APIs the solution is typically implemented using the following HTTP headers:
-
ETag- this HTTP header field is a string that is returned when aGETis requested against a resource. TheETagcontains a representation of the resource at the time theGEToccurred and at its simplest, theETagcan be a version number or a timestamp (although this is best avoided in a distributed environment) but it is more likely to represent a hash of the resource’s payload fields -
If-Match- this HTTP header field is a string that is passed when aPUTis requested against a resource. TheIf-Matchcontains theETagpreviously obtained from the GET request. The server will ensure that thePUTrequest is only performed if the value in theIf-Matchheader matches the derivedETagvalue of the current state of the resource. If the update request cannot be performed due to a mismatch then a 412 HTTP status code must be returned. If theIf-Matchheader is not in thePUTrequest then a 428 HTTP status code must be returned
The following shows how ETag and If-Match headers can be used to avoid concurrency issues:
- consider two users who have performed a
GETagainst a resource e.g.GET /loans/123and they both receive a payload of, for example:{amount = 1000 EUR , status= pending}and anETagvalue = 1 - the first user then modifies the payload and requests an update to the amount with a new payload e.g.
PUT /loans/123 {amount = 1500 EUR , status= pending}withETagvalue = 1 - once the update from the first user has been committed the value of the
Etagvalue will be moved to 2 - the second user also modifies the payload and requests an update to the status with a new payload e.g.
PUT /loans/123 {amount = 1000 EUR , status= approved}withETagvalue = 1 - because the first user has already committed their changes the
ETagvalue would not match that held against the resource and so the approval would be declined - to fix it, second user would need to perform another
GETagainst the modified version of the loan e.g.GET /loans/123to retrieve theETagvalue = 2 and then request the update again
Concurrency API Standards:
The implementation of concurrency using ETag and If-Match is not mandatory for all APIs since it imposes strict rules on the client and server, however, the implications of NOT implementing concurrency must be fully considered especially when backend servers support updates through a variety of different channels in addition to REST APIs, hence:
| Rule Identifier | Description |
|---|---|
| CON-001 | Concurrency MUST be considered for all API requests |
| CON-002 | Concurrency SHOULD be supported for PUT and PATCH requests |
If concurrency is implemented then the following standards apply:
| Rule Identifier | Description |
|---|---|
| PPM-005 RSP-016 | APIs supporting concurrency with optimistic locking MUST define ETag and If-Match headers on associated GET and PUT operations |
| RSP-009 | APIs supporting concurrency with optimistic locking MUST return 412 status code if the If-Match header on a PUT request does not match the derived ETag of the current state of the resource |
| RSP-009 | APIs supporting concurrency with optimistic locking MUST return 428 status code if the If-Match header is not included on a PUT request |
Sample API Code:
The following code snippets show sample OAS2 definitions of GET and PUT operations within an API that supports concurrency:
get:
...
responses:
200:
schema:
$ref: '#/definitions/test
headers:
ETag:
description: Used to cache key for future requests
type: string
put:
operationId: putEntry
parameters:
- name: If-Match
in: header
description: For updates this field needs to be present and contain an ETag value
type: string
required: true
...
responses:
...
412:
description: Precondition Failed - version provided in the If-Match header is invalid
schema:
$ref: '#/definitions/ErrorDescription
428:
description: Precondition Required - version must be provided in the If-Match header
schema:
$ref: '#/definitions/ErrorDescription'
References: